Although treatment with stem cell therapy has been around for decades, it is still widely misunderstood. You may even feel confused about it yourself. One common source of confusion is what stem cells actually are and where they originate.
Located throughout your body, stem cells have the unique ability to transform themselves into several different types of cells through the process of mitosis to produce more cells. As a stem cell divides, every new cell it creates can remain a stem cell or become another type of cell that is more specialized.
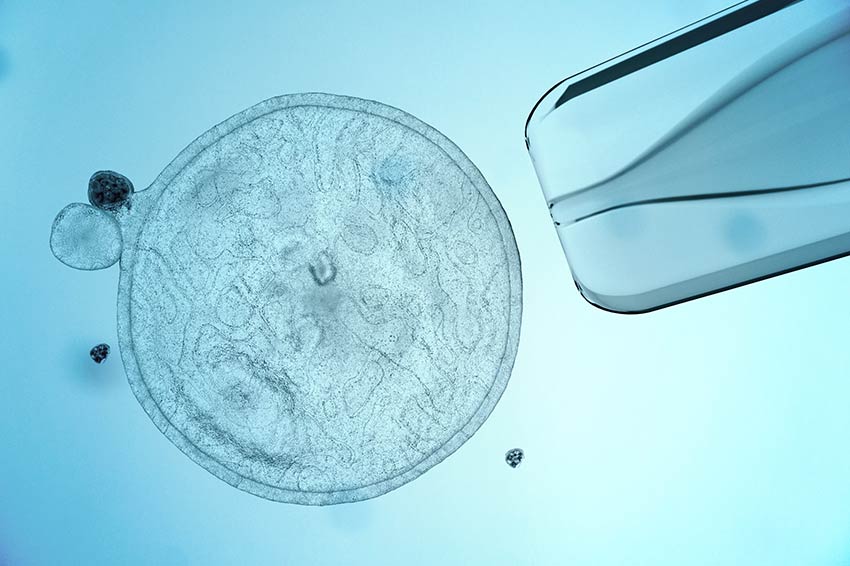
Embryonic stem cells are found in the inner cells of a blastocyst while adult stem cells are located in various tissues in the body. Several sub-types of stem cells exist as well, each with unique properties to promote your healing.
Stem Cell Types
Stem cells used in therapy can come from several different sources: blastocysts created for in-vitro fertilization, umbilical cords donated by parents, adult donors, or your own body. Specialized types of stem cells include:
- Stem cells from blood or umbilical cord: Hematopoietic stem cells are the primary blood cells in your body that produce all other types of blood cells. They can be harvested from the human umbilical cord or circulating blood and are made from mesoderm. They can replicate themselves to create both white and red blood cells that your body needs to maintain a healthy immune system . The treatment of autoimmune diseases and other various chronic diseases with hematopoetic stem cells has shown promising results. Over 30 clinical trials are currently taking place to test the effectiveness of umbilical cord stem cell tissues in treating stroke, heart disease, and spinal cord injuries
- Stem cells from bone marrow: Bone marrow is located inside of your bones in their flexible tissue. It helps create red blood cells at the top of long bones. Bone marrow cells are specialized and can create additional blood-forming cells or transform into a different type of cell. Typically a bone marrow transplant is performed to replace the stem cells that have been destroyed by chemotherapy or radiation.
- Embryonic stem cells: A blastocyst, which forms within three to five days of conception, is made up primarily of stem cells. It can contain as many as 150 unique stem cells prior to implantation. Like the umbilical cord, embryonic stem cells contain powerful healing capabilities and differ from adult stem cells in that they can be endlessly replicated. However, the use of embryonic stem cells in the treatment of disease is considered controversial and ethically questionable.
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Non-hematopoietic stem cells, also known as bone marrow stromal stem cells. These can generate bone, cartilage, and fat cells that support the formation of blood and fibrous connective tissue. These adult stem cells harvested from your fat (called “adipose-derived stem cells”) are known for their high potency and can be used in a variety of regenerative medicine treatment applications, including wound healing, cardiovascular grafts, soft tissue and cartilage repair.
Stem Cells and Stromal Vascular Fraction Treatment
Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF) is the safest and most widely researched treatment available in regenerative medicine today. This is because it uses mesenchymal stem cells sourced from your own fat. An injection of SVF also includes preadipocytes and pericytes that make it extremely effective and potent. SVF is being used to treat various systemic chronic diseases so patients can resume a high quality of life.
Specifically, research studies are currently being conducted to determine how SVF can help treat:
- Asthma and other pulmonary diseases
- Cardiac disease such Congenstive Heart Failure
- Orthopedic bone and joint issues like osteoarthritis and spine disease
- Neurological diseases like Parkinson’s, Muscular Dystrophy, ALS, Multiple Sclerosis and others
- Erectile dysfunction
- Male incontinence
- And many others
Stem cells derived from animals may also be appropriate in your situation. A form of cell therapy called live cell therapy utilizes stem cells found in sheep. While this is a legitimate and well-researched cellular treatment originating in Europe, patients may be easily confused by advertised therapies touted as stem cell therapy, but actually aren’t. These advertised stem cell therapies may actually be platelet rich plasma therapy, or stem cells derived from apples, or amniotic fluid therapy, and may have little to no connection to an actual stem cell therapy.
If you are considering regenerative treatment methods that include stem cell therapy, you owe it to yourself to learn as much as you can.